
Bitumen production process
Follow us on Twitter ![]()
Question, remark ? Contact us at contact@myengineeringtools.com
1. Introduction
2. Bitumen production process
1. Introduction
Bitumen is a main binder in road construction. It can be used to
bond the aggregates well together and form the asphalt.
Different types of bitumen can be used in the flexible pavement. The
main types of bitumen grades are VG bitumen and Pen bitumen which
can be used directly in the hot asphalt.
These two types of bitumen are produced directly from distillation
of crude oil. Generally, bitumen can be obtained by different ways
including straight run, air blowing, semi blowing, solvent
deasphalting and blending.
In the article below which is written by the Infinity Galaxy
team, you can read more details about bitumen production by
air blowing method. Also, the infographic can completely show you
the bitumen production process.
2. Bitumen production process
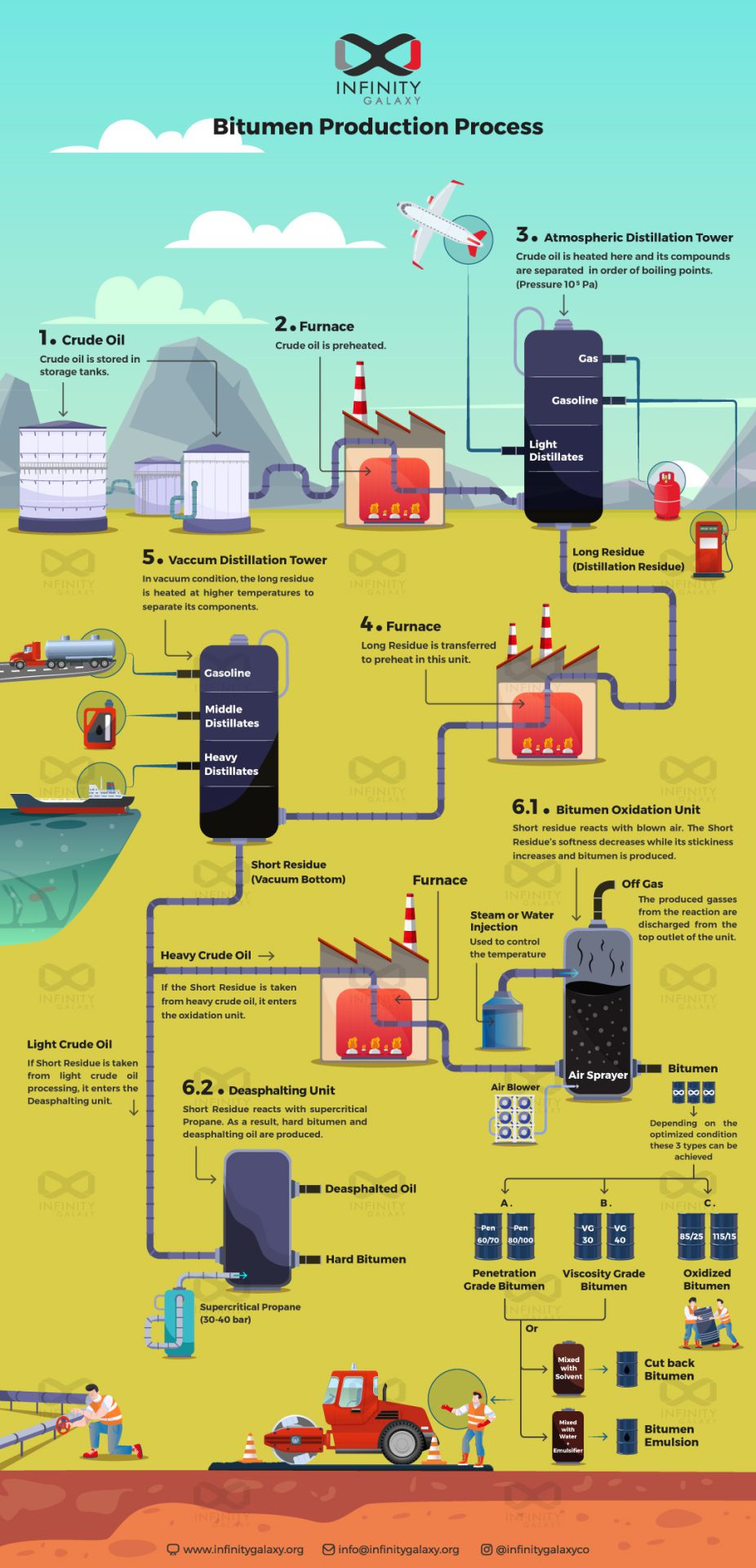
Bitumen production is a complex process that involves several stages
to convert crude oil into the final product suitable for various
applications, particularly in road construction. Understanding the
intricacies of this process is crucial for ensuring the quality and
consistency of the end product.
2.1 Crude Oil Distillation
The journey of bitumen production begins with the refining of crude
oil in a petroleum refinery. Crude oil, extracted from geological
formations, is a mixture of hydrocarbons of varying molecular
weights and compositions. In the first stage of the process, known
as crude oil distillation, the crude oil is heated in a distillation
unit, typically consisting of an atmospheric distillation tower.
As the crude oil is heated, it vaporizes and rises through the
tower, which contains multiple trays or stages. Each tray allows for
the separation of different components of the crude oil based on
their boiling points and molecular weights. Lighter components, such
as gasoline and diesel, vaporize at lower temperatures and are
collected from higher trays, while heavier components, including
bitumen precursors, remain in liquid form and are collected at the
bottom of the tower.
2.2 Vacuum Distillation
After the initial distillation process, the heavier residue known
as "long residue" or "residuum" is further processed in a vacuum
distillation tower. This residual fraction contains high molecular
weight hydrocarbons, including the precursors for bitumen
production. Vacuum distillation is conducted under reduced pressure
to lower the boiling point of the residual fraction, preventing
thermal degradation and reducing the risk of unwanted reactions.
During vacuum distillation, the long residue is heated and
vaporized, allowing for the separation of additional fractions based
on their boiling points. The heaviest fraction obtained from vacuum
distillation is known as "vacuum bottom," which serves as a primary
feedstock for bitumen production.
2.3 Air Blowing and Oxidation
The vacuum bottom obtained from the vacuum distillation tower
undergoes further processing through air blowing and oxidation to
convert it into bitumen. In the air blowing process, the vacuum
bottom is heated and exposed to controlled airflow, typically using
mild air or oxygen. This introduction of air leads to the oxidation
of bitumen precursors, resulting in changes to its chemical
composition and physical properties.
The oxidation process influences critical characteristics of the
final bitumen product, such as its softening point, penetration
degree, and viscosity. Through careful control of process
parameters, different grades of bitumen can be produced to meet
specific performance requirements for various applications,
including road construction.
2.4 Product Refinement and Packaging
Following the air blowing and oxidation steps, the resulting
bitumen undergoes quality control measures to ensure that it meets
industry standards and specifications. Quality testing may include
analyses of viscosity, penetration, ductility, and other physical
properties, as well as assessments of chemical composition and
performance characteristics.
Once the quality of the bitumen is confirmed, it is packaged into
containers suitable for distribution and storage. Common packaging
options include new steel drums or jumbo bags, which protect the
bitumen from contamination and ensure its integrity during
transportation to end-users, such as construction companies and
infrastructure developers.
3. Benefits of Air Blowing Method
The air blowing method, also known as the oxidation process, plays a pivotal role in the production of bitumen from vacuum bottom obtained during crude oil refining. This method offers several distinct advantages over alternative processes, making it a preferred choice for bitumen manufacturers. Understanding the benefits of the air blowing method is essential for optimizing bitumen production processes and enhancing product quality.
3.1 Enhanced Control over Bitumen Properties
One of the primary advantages of the air blowing method is its ability to provide precise control over the properties of the resulting bitumen. By adjusting key parameters such as temperature, airflow rate, and reaction time, manufacturers can tailor the characteristics of the bitumen to meet specific performance requirements. This level of control allows for the production of bitumen grades with varying viscosity, penetration, softening point, and other critical attributes, ensuring compatibility with diverse applications in road construction and other industries.
3.2 Modification of Physical and Chemical Properties
The oxidation process facilitated by air blowing induces significant changes in the molecular structure of bitumen precursors present in the vacuum bottom feedstock. Through controlled exposure to air or oxygen, chemical reactions occur, leading to the formation of oxygen-containing functional groups within the bitumen matrix. These structural modifications impart desirable properties to the bitumen, such as improved elasticity, adhesion, and resistance to aging and weathering. Additionally, oxidation facilitates the enhancement of thermal stability and rheological properties, further enhancing the performance and durability of the final bitumen product.
3.3 Versatility in Bitumen Grade Production
Another key benefit of the air blowing method is its versatility in producing a wide range of bitumen grades to suit varying application requirements. By manipulating process parameters and reaction conditions, manufacturers can generate different viscosity grades, penetration grades, and performance grades of bitumen. This flexibility allows for the customization of bitumen products tailored to specific climate conditions, traffic loads, and pavement specifications. Furthermore, the air blowing method enables the production of specialized bitumen variants, such as modified bitumen and polymer-modified bitumen, which exhibit enhanced properties for specialized applications in high-traffic areas, extreme weather environments, and challenging construction scenarios.
3.4 Environmental and Economic Considerations
In addition to its technical advantages, the air blowing method offers environmental and economic benefits compared to alternative bitumen production processes. The oxidation process consumes relatively less energy and generates fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to alternative methods such as solvent extraction or thermal cracking. Furthermore, the utilization of vacuum bottom, a by-product of crude oil refining, as the primary feedstock for bitumen production enhances resource efficiency and reduces waste disposal requirements. Overall, the air blowing method contributes to sustainable manufacturing practices while maintaining cost competitiveness in the bitumen industry.
4. Quality Control and Testing Procedures
Ensuring the quality and consistency of bitumen products is paramount in meeting the stringent performance requirements of infrastructure projects, particularly in road construction. Quality control measures and rigorous testing procedures are integral components of the bitumen production process, allowing manufacturers to assess and verify the physical, chemical, and performance characteristics of the final product. This section provides an overview of the key quality control and testing procedures employed in bitumen production facilities.
4.1 Physical Properties Testing
Physical properties testing encompasses a range of analyses aimed
at evaluating the fundamental characteristics of bitumen related to
its mechanical behavior, durability, and suitability for specific
applications. Common physical properties tests conducted on bitumen
samples include:
Penetration Test: This test measures the consistency of bitumen by
determining the depth to which a standard needle penetrates the
material under specified conditions. Penetration values indicate the
hardness or softness of bitumen and are used to classify bitumen
into penetration grade categories.
Softening Point Test: The softening point of bitumen is determined
using methods such as the ring and ball apparatus, indicating the
temperature at which the bitumen softens and flows under
standardized conditions. This parameter is crucial for assessing the
temperature susceptibility and thermal stability of bitumen in
pavement applications.
Ductility Test: Ductility represents the ability of bitumen to
stretch without breaking and is evaluated by measuring the
elongation of a bitumen sample before failure under tension.
Ductility values provide insights into the flexibility and
deformation resistance of bitumen at different temperatures and
loading conditions.
Viscosity Test: Viscosity is a measure of bitumen's resistance to
flow and deformation, affecting its handling characteristics and
coating ability. Various viscosity testing methods, including
rotational viscometry and capillary viscometry, are employed to
quantify bitumen viscosity at specific temperatures and shear rates.
4.2 Chemical Composition Analysis
Chemical composition analysis plays a crucial role in assessing the
purity, stability, and performance-enhancing additives present in
bitumen formulations. Advanced analytical techniques are utilized to
characterize the molecular structure and functional groups within
bitumen samples, including:
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS): GC-MS analysis allows
for the identification and quantification of individual hydrocarbon
components present in bitumen, facilitating the determination of
molecular weight distribution, aromaticity, and heterogeneity.
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR): FTIR spectroscopy
provides insights into the chemical bonding and functional groups
present in bitumen molecules, enabling the detection of oxidation
products, polymer additives, and other chemical modifiers.
4.3 Performance Testing
Performance testing evaluates the functional properties of bitumen
related to its behavior under simulated service conditions, such as
traffic loading, temperature variations, and moisture exposure.
Performance tests assess key parameters, including:
Rheological Properties: Dynamic Shear Rheometer (DSR) and Bending
Beam Rheometer (BBR) tests measure the viscoelastic behavior and
stiffness characteristics of bitumen at different temperatures and
loading frequencies, reflecting its deformation resistance and
fatigue performance.
Aging Resistance: Thin Film Oven Test (TFOT) and Pressure Aging
Vessel (PAV) tests simulate the effects of short-term and long-term
aging on bitumen samples, assessing their resistance to oxidative
aging, hardening, and embrittlement over time.
4.4 Quality Assurance Protocols
In addition to laboratory testing, quality assurance protocols are
implemented throughout the bitumen production process to ensure
compliance with industry standards and specifications. Quality
assurance measures include:
Process Control Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of process
parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and flow rates, ensures
the consistent production of bitumen with predetermined properties
and characteristics.
Batch Sampling and Analysis: Regular sampling of bitumen batches at
various stages of production allows for real-time quality assessment
and adjustment of process parameters to maintain product consistency
and integrity.
Certification and Compliance: Bitumen products undergo third-party
certification and compliance testing to validate their conformity
with national and international standards, ensuring their
suitability for use in construction projects and infrastructure
applications.