
Centrifugal pump minimum required flow
What is the minimum flow of a pump ?
Why a recirculation is important and why to ensure a minimal flow ?
How to calculate the required minimum flow of a pump ?
Follow us on Twitter ![]()
Question, remark ? Contact us at contact@myengineeringtools.com
| Section summary |
|---|
| 1. What is a minimum
flow for a pump |
| 2. How to calculate
a centrifugal pump minimal flow |
| 3. Pump minimum flow free calculator |
1. What is the minimum flow for a pump ?
Due to the rotation of the impeller, energy is transferred to the fluid in a centrifugal pump. Part of this energy is actually dissipated in heat. If the flow through the pump is too low, the fluid temperature may increase and reach the saturation temperature at the pressure within the pump, leading to cavitation and damages of the pump. It is therefore necessary to ensure a minimal flow through a centrifugal pump. This minimum flow can be done thanks to a recirculation.2. How to calculate a centrifugal pump minimal flow ?
The minimum flow to ensure with a centrifugal pump can be calculated the following way :3. Pump minimum flow free calculator
Warning : this calculator is provided to illustrate the concepts mentioned in this webpage, it is not intended for detail design. It is not a commercial product, no guarantee is given on the results. Please consult a reputable designer for all detail design you may need.
3.1 Excel calculator
You can
download the calculator here : link
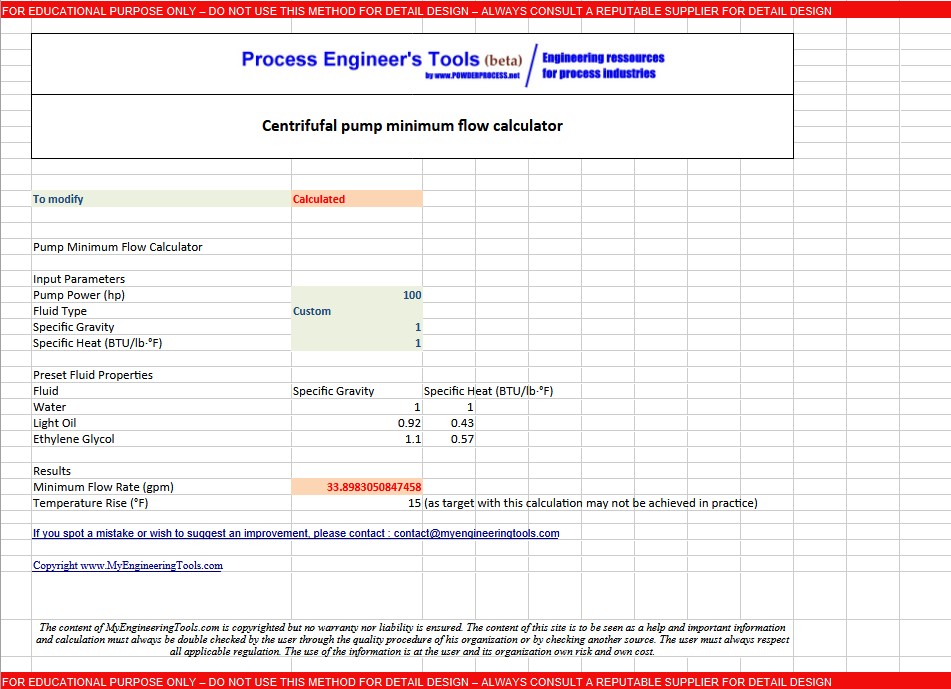
3.2 Online
calculator
Pump Minimum Flow Calculator
⚠️ Important Safety Notes:
- This calculator provides theoretical minimum flow values
- Always consult pump manufacturer's specifications
- Operating below minimum flow can cause severe damage
Results
FAQ: Centrifugal Pump Minimum Required Flow
1. What is the minimum flow for a centrifugal pump?
The minimum flow for a centrifugal pump is the lowest flow rate required to prevent issues like overheating, cavitation, and damage to the pump components. It ensures safe and efficient operation.
2. Why is recirculation important in centrifugal pumps?
Recirculation ensures a minimum flow through the pump, preventing low-flow conditions that can lead to heat dissipation, cavitation, and potential damage to the impeller and bearings.
3. How is the minimum flow calculated for a centrifugal pump?
The minimum flow can be estimated using the formula: \[ q = \frac{P}{2.95 \times C_p \times sg} \] Where: - \( q \) = Minimum flow rate (gpm) - \( P \) = Pump power (bhp) - \( C_p \) = Specific heat capacity (Btu/lb·°F) - \( sg \) = Specific gravity of the fluid.
4. What are the risks of operating below the minimum flow?
Operating below the minimum flow can cause cavitation, overheating, and mechanical stress, leading to premature wear and potential failure of pump components.
5. Can the calculated minimum flow be used without verification?
No, the calculated minimum flow is an estimation. Always consult the pump manufacturer's specifications to ensure accuracy and safety.
6. What factors influence the minimum flow requirement?
Factors include pump power, fluid properties (specific heat capacity and specific gravity), and operating conditions. Each pump model may have unique requirements.
7. How can I ensure my pump operates above the minimum flow?
Implement a recirculation system or bypass line to maintain flow rates above the minimum threshold, especially during low-demand periods.
8. Are there tools available to calculate minimum flow?
Yes, our website offers a free online calculator and an Excel tool to estimate the minimum flow for centrifugal pumps.
9. What precautions should be taken when using the calculator?
The calculator provides theoretical values. Always verify results with the pump manufacturer and ensure compliance with safety standards.
10. Why is cavitation a concern in centrifugal pumps?
Cavitation occurs when the fluid temperature reaches its saturation point, forming vapor bubbles that collapse and damage the impeller and other components. Maintaining minimum flow prevents this.