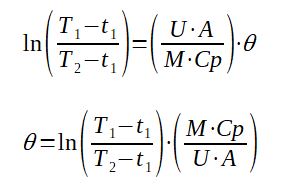Tank heating & cooling time : step by step calculation
guide
Time required for batch heating or cooling using an internal coil
Follow us on Twitter ![]()
Question, remark ? Contact us at contact@myengineeringtools.com
| Section summary |
|---|
| 1. STEP 1 : Get the
design data |
| 2. STEP 2 : Apply
the heat transfer equation |
| 3. Tank cooling time |
| 4. STEP by STEP Example |
| 5. Free Excel calculation tool for tank
heating or cooling time calculation |
This page is giving a calculation method to determine the time required to heat up a tank equipped with an internal heating coil.
Introduction tank heating
Tank heating is required in many process applications. For example in chemical industries, batch reactors are often equipped with an internal coil which will increase the temperature to an optimal level for the reaction to happen.
The Engineer, when designing or operating the tank must then calculate how long it will take to heat up the reactor.
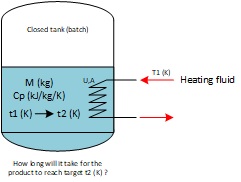
Assumptions :
- The heating fluid is isothermal
- The heating of the tank structure is negligible compared to the heating required for the material, and the heat losses are negligible (-> formula valid for large batches)
- The heat exchanger involved in heating is an internal coil
1. STEP 1 : Get the design data
The following data must be gathered in order to perform the calculation :
Sizing data of the heating coil :
- The overall heat transfer coefficient of the heating coil
- The heat exchange area of the heating coil
Process operation parameters :
- Temperature of the heating fluid (assumed here to be isotherm)
- The initial tank temperature (temperature at beginning of heating)
- The target tank temperature (temperature at end of heating)
- The batch size / weight
- The specific heat of the material to be heated up
2. STEP 2 : Apply the heat transfer equation
The following formula is applied to calculate the increase of temperature of the material in the tank over time [Chopey] :
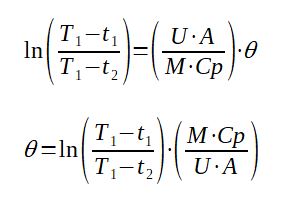
With :
T1 = Temperature of the heating fluid (K)
t1 = Initial tank temperature (K)
t2 = target tank temperature (K)
U = overall heat transfer coefficient of the internal heating coil
(W/m2.K)
A = heat exchange area of the internal heating coil (m2)
M = weight of material to heat in the tank (kg)
Cp = specific heat of the material (kJ/kg/K)
θ = time required to heat up the tank (s)
3. Tank cooling time
Tank cooling time can be calculated by using the same formula as above but changing the temperatures as the batch temperature becomes the hot source while the cold source is the cooling media.
The same assumptions are required to make the calculation meaningful (isothermal cooling fluid, large batch, internal cooling coil).
The tank cooling time can be calculated thanks to the following equation :
With :
t1 = Temperature of the cooling fluid (K)
T1 = Initial tank temperature (K)
T2 = target tank temperature (K)
U = overall heat transfer coefficient of the internal cooling coil
(W/m2.K)
A = heat exchange area of the internal cooling coil (m2)
M = weight of material to cool in the tank (kg)
Cp = specific heat of the material (kJ/kg/K)
θ = time required to cool down the tank (s)
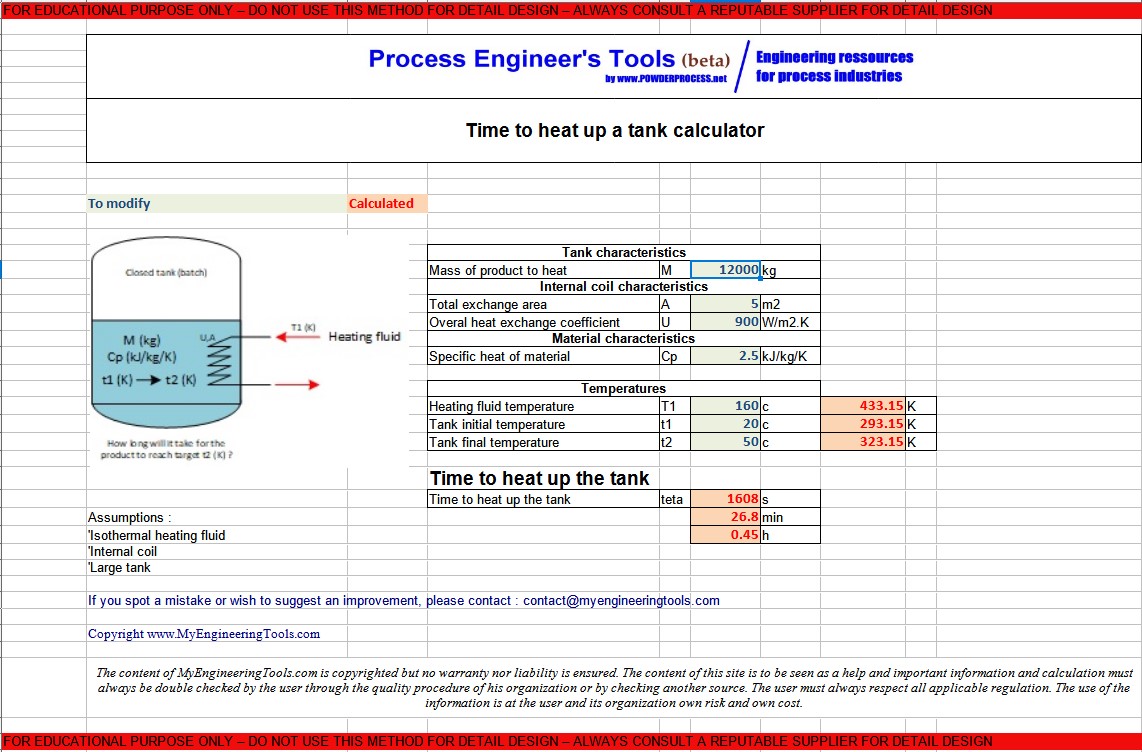
4. STEP by STEP Example : time to heat up a tank
The following tank must be heated up from 20°c to 50°c :
- The tank contains 12 tons of material
- The material has a specific heat capacity of 2.4 kJ/kg/K
- The heating coil is 5 m2 and the overal heat transfer coefficient has been estimated from previous trials at 900 W/m2.K
- The heating coil is using condensing steam at 433 K
How long will it take to heat up the material in the tank ?
STEP 1 : Get the required data
T1 = Temperature of the heating fluid (K) = 433 K
t1 = Initial tank temperature (K) = 20+273.15 = 293.15 K
t2 = target tank temperature (K) = 50+273.15 = 323.15 K
U = overall heat transfer coefficient of the heating coil (W/m2.K)
= 900 W/m2.K
A = heat exchange area of the heating coil (m2) = 5 m2
M = weight of material to heat in the tank (kg) = 12000 kg
Cp = specific heat of the material (kJ/kg/K) = 2.4 kJ/kg/K
STEP 2 : Apply the heat transfer equation
ln ((T1 - t1)/(T1-t2)) = ln ((433-293.15)/(433-323.15)) = 0.2415
MCp / UA = (12000 * 2400) / (900*5) = 6400
teta = 0.2415*6400 = 1545 s = 25.76 min = 0.43 h
5. Free Excel calculation tool for
tank heating time calculation
The time to heat up a tank can be calculated thanks to this free
Excel calculator : Calculation Tool - tank heating or cooling
time calculator (click here)
Warning : this calculator is provided to illustrate the concepts mentioned in this webpage, it is not intended for detail design. It is not a commercial product, no guarantee is given on the results. Please consult a reputable designer for all detail design you may need.
Sources
[Chopey] Handbook of Chemical Engineering calculations, Chopey et al, McGraw Hill, 2004