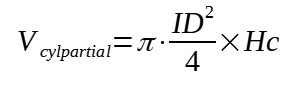Volume of a vertical cylinder tank : step by step calculation guide
How to calculate the volume of a vertical cylindrical vessel
Follow us on Twitter ![]()
Question, remark ? Contact us at contact@myengineeringtools.com
1. Vertical cylindrical tank
4. Excel vertical tank volume calculator
1. Vertical cylindrical tank
Vertical cylindrical tanks are used to store liquids in process industries such as chemicals, petrochemicals or oil. They allow to keep a minimal footprint while allowing large storage volumes. A vertical cylindrical vessel is made of cylindrical shell and of 2 ends that can take different standard shapes.
With :
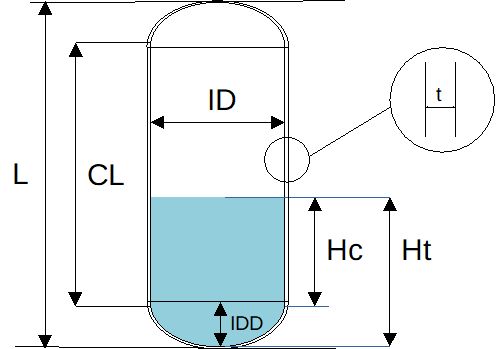
ID = tank internal diameter (m)
OD : tank outside diameter (m) = ID+2*t
Ht = total height of liquid in the tank (m)
Hc = height of liquid in the cylindrical part of the tank (m)
IDD = tank head internal depth (m)
L = total length of the vessel (m), this includes as well the
thickness of the metal (2*t)
CL = length of the cylindrical section of the tank (m), this
includes the straight flanged portion of the tank heads
t = thickness of the shell (m), it is assumed that the thickness is
the same everywhere
The tank heads can have the following shapes :
- Flat head
- Hemispheric
- Ellispoidal (standard proportions with z = D/4)
- Torispherical (Flanged and dished tank head ASME 80:10)
- Standard dished (not ASME compliant for pressurized vessels)
- Other shapes are possible but only the most common are given in this page
For the calculations presented it is assumed that both heads of the vessel are identical.
This page is explaining how to calculate the volume in the tank as
a function of the level of liquid H.
Top 5 Most Popular
1. Compressor
Power Calculation
2. Pump Power Calculation
3. Pipe Pressure
Drop Calculation
4. Fluid Velocity in pipes
5. Churchill Correlation
(friction factor)
2. Volumes calculation formulae
Please express all length in m to get m3 as result of the calculations
2.1 Cylindrical section of the tank
2.1.1 Total volume of the cylindrical shell of the vessel
The total volume of a cylinder is given by the following formula :
Vcyl_total = π.ID2/4*CL
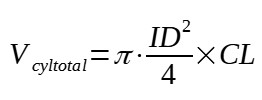
2.1.2 Partial volume horizontal cylinder
The actual volume in the cylinder actually depends on the height of liquid H in the cylindrical part of the tank, it thus necessary to just replace the total cylindrical shell length L by the actual height of liquid Hc in the formula above. The partial volume filled can be calculated with the following equation :
Vcylpartial = π*ID2/4*Hc
Note that in the case of flat heads
tank, the volume calculated above is directly the volume of
liquid in the tank, no need to go to step 2. This is is however an
approximation as there is always some kind of curvature in between
the flat head and the cylindrical shell.
2.2 Volume of tank heads
2.2.1 Bottom head
The general formula to calculate the partial volume filled in the bottom head of the tank is the following [Wiencke] :
Vbottom_head_partial = π/6*[(3*ID*H2)/c - (2*H3)/c2]
This formula is valid when the total height of liquid is below the height of the bottom head : 0 <= H <= IDD
The parameter c depends on the type of standard head and is defined in the table in paragraph 2.2.3
2.2.2 Top head
The general formula to calculate the partial volume filled in the top head of the tank is the following [Wiencke] :
Vtop_head_partial = π/12*[3*ID2*H - (4*H3)/c2]
This formula is valid when the total height of liquid is above the cylindrical shell height and starts to reach the to head : 0 <= (H-IDD-CL) <= IDD
The parameter c depends on the type of standard head and is defined in the table in paragraph 2.2.3
2.2.3 Partial volume depending on standard shape of tank heads
The formula above are using the parameters c and the inside dish depth of the head (IDD). Those parameters are changing depending on the tank head used. c and IDD are tabulated depending on the tank head shape, the values to use in the formulae above are given in the table below [Wiencke] :
| Vessel head standard shape | c | IDD |
| ASME 2:1 elliptical head | 1/2 | ID/4 |
| Hemispherical head | 1 | ID/2 |
| Flat head | 0 | 0 |
| ASME torispherical head (R=OD, r=min 0.06*OD) |
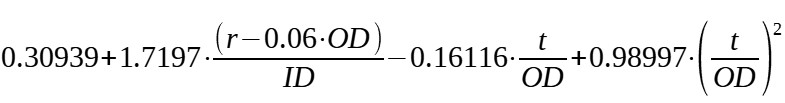 |
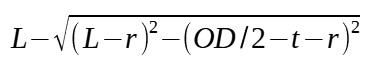 |
| DIN torispherical head (R=OD, r= 0.1*OD) |
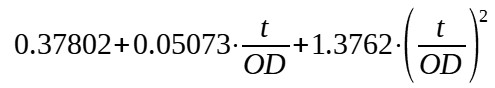 |
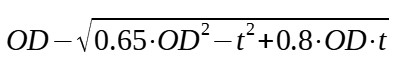 |
| DIN semi ellipsoidal head (R=0.8*OD, r=0.154*OD) |
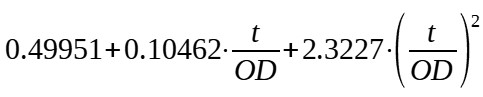 |
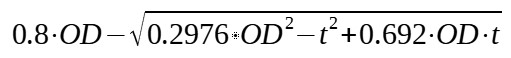 |
With :
R = Inside crown radius of head (m)
r = Inside knuckle radius (m)
3. Step by step calculation of the volume of a vertical tank
3.1 Step 1 : Determine the height of liquid H
The height of liquid can lead to 3 different cases :
-
Case 1 : The liquid level is low, within the bottom head of the vessel : 0 <= H <= IDD
-
Case 2 : The liquid level is within the cyclindrical section of the vessel : IDD < H < CL
-
Case 3 : The liquid level is reaching the top head of the vessel : CL+IDD < H < CL+2*IDD
3.2 Step 2 : Calculate the volume of liquid in the bottom head of the tank
-
If 0 <= H <= IDD (case 1)
The bottom head is partially or totally filled. The formula in paragraph 2.2.1 can be used :
Vbottom_head = π/6*[(3*ID*H2)/c - (2*H3)/c2]
Refer to table 2 to determine c and IDD for the geometry of the tank used.
-
If H > IDD (case 2 and 3)
Refer to table 1 to determine directly the volume of the filled head, of calculate it via the formula of paragraph 2.2.2.1 by consdering H = IDD.
3.3 Step 3 : Calculate the volume of liquid in the cylindrical section of the tank
-
If 0 <= H <= IDD (case 1)
The level is not reaching the cylindrical section, volume in the cylindrical section is 0.
-
If IDD < H <= CL (case 2)
The level is somewhere within the cylindrical section of the vessel. Refer to formula of paragraph 2.1.2 by considering Hc = H-IDD.
- If CL+IDD < H <= CL+2*IDD (case 3)
The level of liquid is reaching the top head : the cylindrical shell is full. The total volume of the cylinder can be calculated with the formula 2.2.1 with H = CL.
3.4 Step 4 : Calculate the volume of liquid in the top head of the tank
- If H <= CL+IDD (case 1 and 2)
The top head of the tank is not holding any liquid, the volume of liquid in the top head is 0.
- If CL+IDD < H <= CL+2*IDD
The top head is partially or totally filled. The formula in paragraph 2.2.2 can be used :
Vtop_head = π/12*[3*ID2*H - (4*H3)/c2]
Refer to table 2 to determine c and IDD for the geometry of the tank used.
3.5 Step 5 : calculate the total volume of liquid in the tank
The total volume of liquid in the tank is equal to the sum of the volumes calculated at step 2, 3 and 4 :
Vtotal = Vbottom_head + Vcylinder + Vtop_head
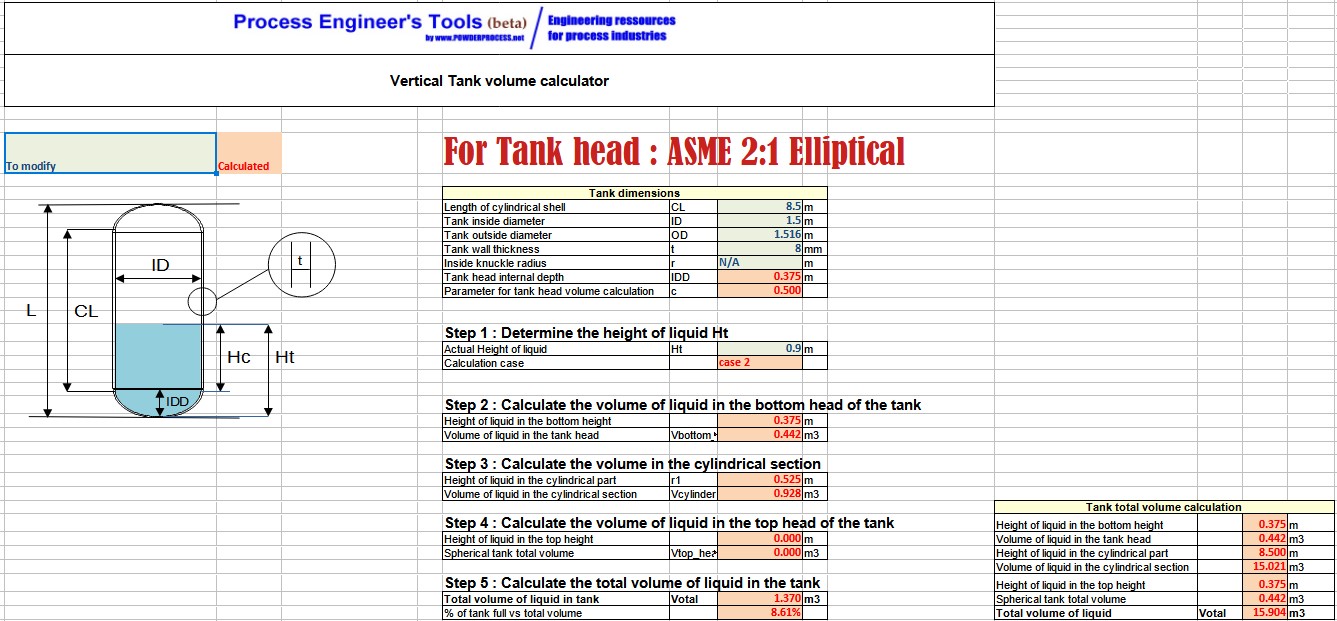
4. Excel vertical tank volume calculator
You can download a calculator to compute the volume of a partially filled vertical tank : Excel calculation tool.
Warning : this calculator is provided to illustrate the concepts mentioned in this webpage, it is not intended for detail design. It is not a commercial product, no guarantee is given on the results. Please consult a reputable designer for all detail design you may need.
Sources